
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Incidence and Prevalence of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus among Korean Children and Adolescents between 2007 and 2017: An Epidemiologic Study Based on a National Database
- Hyun Wook Chae, Gi Hyeon Seo, Kyungchul Song, Han Saem Choi, Junghwan Suh, Ahreum Kwon, Sangmi Ha, Ho-Seong Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):866-874. Published online November 4, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0212
- 7,750 View
- 319 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 29 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) among children is high in Europe and the USA and relatively low in Asia, including Korea. The present study aimed to investigate the incidence and prevalence of childhood-onset T1DM in Korea and examine trends in incidence.
Methods
This study was conducted using the national registry data provided by the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service in Korea from 2007 to 2017. We included children aged 0 to 14 years who were newly registered with a T1DM diagnosis each year (code E10).
Results
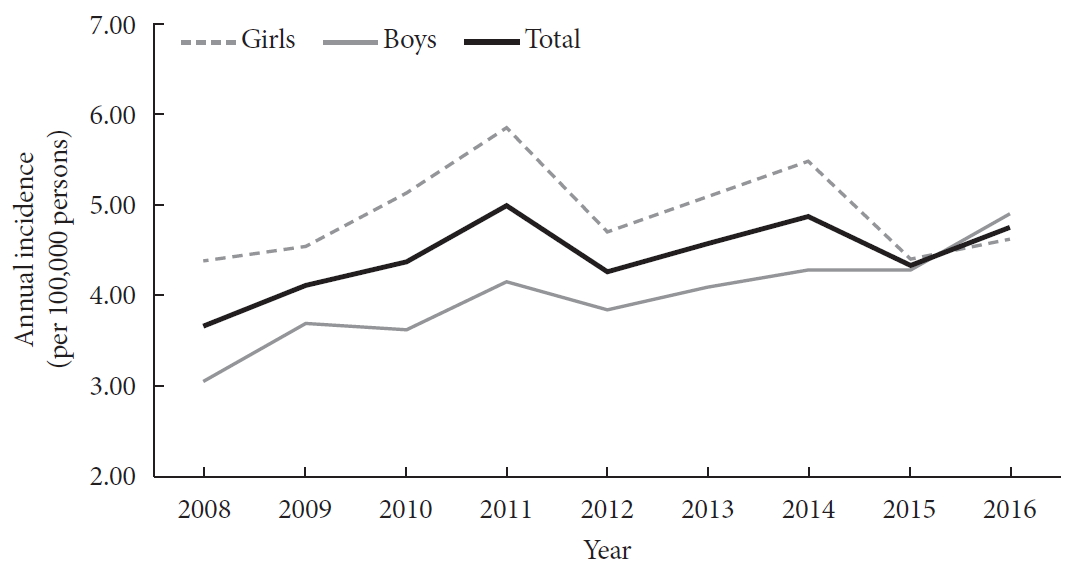
A total of 29,013 children were registered. The overall incidence of T1DM was 4.45 per 100,000 persons (girls, 4.93; boys, 4.01). The overall incidence of childhood-onset T1DM in Korea increased from 3.70 in 2008 to 4.77 in 2016 (P=0.002). The incidence of T1DM increased from 3.07 in 2008 to 4.89 in 2016 (P<0.001) among boys. Although the incidence of the disease increased significantly among boys aged 5–9 and 10–14 years, it remained constant among girls (4.39 in 2008, 4.64 in 2016). The overall prevalence of childhood-onset T1DM in Korea increased from 32.85 in 2007 to 41.03 per 100,000 persons in 2017 (girls, 35.54 to 43.88; boys, 32.85 to 41.03).
Conclusion
We calculated relatively accurate incidence and prevalence of childhood-onset T1DM from a nation-based registry. The incidence increased by 3% to 4% every year from 2007 to 2017. The increasing trend is noteworthy compared with previous reports. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of non-thyroidal autoimmune diseases in patients with Graves’ disease: a nationwide retrospective cohort study
Seo Young Sohn, Jiyeon Ahn, Min Kyung Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee, Ji-Won Kwon, Ji-Min Kweon, Ju-Yeun Lee
Rheumatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Non-pharmacological Interventions for Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes in the Last Five Years: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
DaeEun Lee, Haejung Lee, YoonYoung Shin, Gaeun Park
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(1): 51. CrossRef - Development and Testing of the School Healthcare Partnership Scale for Parents
Ju-Yeon Uhm, Suhee Kim
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2024; 46(3): 219. CrossRef - Trends in incidence rates of childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective study in Isfahan province, Iran
Mahin Hashemipour, Mohammadreza Maracy, Shaghayegh Haghjooy Javanmard, Farzane Zamaneh, Neda Mostofizadeh, Silva Hovsepian
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(3): 376. CrossRef - Incidence of Childhood Type 1 Diabetes in Beijing During 2011–2020 and Predicted Incidence for 2025–2035: A Multicenter, Hospitalization-Based Study
Yuchuan Li, Kun Qian, Di Wu, Xinli Wang, Hong Cui, Geheng Yuan, Jinfang Yuan, Lijun Yang, Liya Wei, Bingyan Cao, Chang Su, Xuejun Liang, Min Liu, Wenjing Li, Miao Qin, Jiajia Chen, Xi Meng, Rui Wang, Shan Su, Xiaobo Chen, Hui Chen, Chunxiu Gong
Diabetes Therapy.2023; 14(3): 519. CrossRef - Utilization of nutrition labels and related factors among patients with diabetes in Korea
So-Jung Lee, Mi Ah Han, Jong Park, So Yeon Ryu
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(2): 297. CrossRef - Long-term trends of pediatric type 1 diabetes incidence in Japan before and after the COVID-19 pandemic
Fumika Matsuda, Tomoyo Itonaga, Miwako Maeda, Kenji Ihara
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The burdens faced by parents of preschoolers with type 1 diabetes mellitus: an integrative review
Sunyeob Choi, Hyewon Shin
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(3): 166. CrossRef - Hypoglycemic Effect of an Herbal Decoction (Modified Gangsimtang) in a Patient with Severe Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Refusing Oral Anti-Diabetic Medication: A Case Report
Sungjun Joo, Hyonjun Chun, Jisu Lee, Seungmin Seo, Jungmin Lee, Jungtae Leem
Medicina.2023; 59(11): 1919. CrossRef - Improving self-management and diabetes indicators in adolescents with type 1 diabetes through self-care education
Narges Asghari, Bahman Dashtebozorgi, Shahnaz Rostami, Saeed Ghanbari, Kourosh Riahi-Ghahfarokhi
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2023; 12(10): 2322. CrossRef - Механізм дії та особливості застосування холекальциферолу в дітей та підлітків на етапах розвитку цукрового діабету 1-го типу
V.V. Popova, N.V. Het´man, Ya.I. Labanets, H.V. Kulikovs´ka, O.V. Furmanova, K.P. Zak
Endokrynologia.2023; 28(1): 36. CrossRef - Comparison of Initial Presentation of Pediatric Diabetes Before and During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Era
Yoonha Lee, Minseung Kim, Kyeongeun Oh, Eungu Kang, Young-Jun Rhie, Jieun Lee, Yong Hee Hong, Young-Lim Shin, Jae Hyun Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent information on test utilization and intraindividual change in anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody in Korea: a retrospective study
Rihwa Choi, Wonseo Park, Gayoung Chun, Jiwon Lee, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(3): e002739. CrossRef - Comparison of the clinical characteristics and outcomes of pediatric patients with and without diabetic ketoacidosis at the time of type 1 diabetes diagnosis
Young-Jun Seo, Chang Dae Kum, Jung Gi Rho, Young Suk Shim, Hae Sang Lee, Jin Soon Hwang
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 27(2): 126. CrossRef - Prevalence trends of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents in North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous federal state in Germany, 2002-2020
C. Baechle, A. Stahl-Pehe, N. Prinz, T. Meissner, C. Kamrath, R.W. Holl, J. Rosenbauer
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 190: 109995. CrossRef - Diabetic ketoacidosis in children with new-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus: demographics, risk factors and outcome: an 11 year review in Hong Kong
Sarah Wing-yiu Poon, Joanna Yuet-ling Tung, Wilfred Hing-sang Wong, Pik-to Cheung, Antony Chun-cheung Fu, Gloria Shir-wey Pang, Sharon Wing-yan To, Lap-ming Wong, Wai-yu Wong, Suk-yan Chan, Ho-chung Yau, Wing-shan See, Betty Wai-man But, Shirley Man-yee W
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 35(9): 1132. CrossRef - School Nurse–Parent Partnership in School Health Care for Children with Type 1 Diabetes: A Hybrid Method Concept Analysis
Ju-Yeon Uhm, Mi-Young Choi
Asian Nursing Research.2022; 16(5): 282. CrossRef - Increased Incidence of Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis After COVID-19: A Two-Center Retrospective Study in Korea
Min Jeong Han, Jun Ho Heo
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 783. CrossRef - Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:46-54)
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 277. CrossRef - Relationships between emissions of toxic airborne molecules and type 1 diabetes incidence in children: An ecologic study
Agostino Di Ciaula, Piero Portincasa
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(5): 673. CrossRef - Diagnosis and management of pediatric type 1 diabetes mellitus
Jieun Lee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2021; 64(6): 425. CrossRef - Diabetes in Adolescence, Appropriate Transition to Adult Clinic
Jieun Lee, Jae Hyun Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(2): 77. CrossRef - Trajectories in glycated hemoglobin and body mass index in children and adolescents with diabetes using the common data model
Yun Jeong Lee, Sooyoung Yoo, Soyoung Yi, Seok Kim, Chunggak Lee, Jihoon Cho, Soyeon Ahn, Sunkyu Choi, Hee Hwang, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Hyung-Jin Yoon, Kwangsoo Kim, Eunhye Song, Jin Ho Choi, Han Wook Yoo, Young-Hak Kim, Ji Seon Oh, Eun-Ae Kang, Ga
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - What Affects Quality of Life for People with Type 1 Diabetes?: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study
Mi-Kyoung Cho, Mi-Young Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(14): 7623. CrossRef - The Relationship between Diabetes Family Conflict and Parental Conflict on Problem Recognition in Illness Self-Management among Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Mi-Kyoung Cho, Mi Young Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(17): 8914. CrossRef - Relationship between Diabetes Family Conflicts or Problem Recognition in Illness Self-Management and Quality of Life of Adolescents with T1DM and Their Parents
Mi-Kyoung Cho, Mi Young Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(20): 10710. CrossRef - Current Advances of Artificial Pancreas Systems: A Comprehensive Review of the Clinical Evidence
Sun Joon Moon, Inha Jung, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 813. CrossRef - History of insulin treatment of pediatric patients with diabetes in Korea
Jae Hyun Kim, Choong Ho Shin, Sei Won Yang
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 26(4): 237. CrossRef - A Position Statement of the Utilization and Support Status of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Korea
Won Jun Kim, Jae Hyun Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Jang Won Son, Ah Reum Khang, Su Kyoung Kwon, Ji Hye Kim, Tae Ho Kim, Ohk Hyun Ryu, Kyeong Hye Park, Sun Ok Song, Kang-Woo Lee, Woo Je Lee, Jung Hwa Jung, Ho-Chan Cho, Min Jeong Gu, Jeongrim Lee, Dal Lae Ju, Yeon Hee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 225. CrossRef
- Risk of non-thyroidal autoimmune diseases in patients with Graves’ disease: a nationwide retrospective cohort study
- Response: Increased Risk of Hospitalization for Heart Failure with Newly Prescribed Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Pioglitazone Using the Korean Health Insurance Claims Database (
Diabetes Metab J 2015;39:247-52) - Sunghwan Suh, Gi Hyeon Seo, Chang Hee Jung, Mee-Kyoung Kim, Sang-Man Jin, You-Cheol Hwang, Byung-Wan Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(4):350-351. Published online August 17, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.4.350
- 3,239 View
- 29 Download
- Increased Risk of Hospitalization for Heart Failure with Newly Prescribed Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Pioglitazone Using the Korean Health Insurance Claims Database
- Sunghwan Suh, Gi Hyeon Seo, Chang Hee Jung, Mee-Kyoung Kim, Sang-Man Jin, You-Cheol Hwang, Byung-Wan Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(3):247-252. Published online April 22, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.3.247
- 3,999 View
- 35 Download
- 21 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We assessed the association of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP4i) with hospitalization for heart failure (HF) using the Korean Health Insurance claims database.
Methods We collected data on newly prescribed sitagliptin, vildagliptin, and pioglitazone between January 1, 2009 and December 31, 2012 (mean follow-up of 336.8 days) to 935,519 patients with diabetes (518,614 males and 416,905 females) aged 40 to 79 years (mean age of 59.4 years).
Results During the study, 998 patients were hospitalized for primary HF (115.7 per 100,000 patient-years). The incidence rate of hospitalization for HF was 117.7 per 100,000 per patient-years among patients on pioglitazone, 105.7 for sitagliptin, and 135.8 for vildagliptin. The hospitalization rate for HF was greatest in the first 30 days after starting the medication, which corresponded to a significantly higher incidence at days 0 to 30 compared with days 31 to 360 for all three drugs. The hazard ratios were 1.85 (pioglitazone), 2.00 (sitagliptin), and 1.79 (vildagliptin). The incidence of hospitalization for HF did not differ between the drugs for any time period.
Conclusion This study showed an increase in hospitalization for HF in the initial 30 days of the DPP4i and pioglitazone compared with the subsequent follow-up period. However, the differences between the drugs were not significant.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cardioprotective effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors versus sulfonylureas in addition to metformin: A nationwide cohort study of patients with type 2 diabetes
Jui Wang, Hon-Yen Wu, Kuo-Liong Chien
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(3): 101299. CrossRef - Changing Fields-Diabetes Medications Invading the Cardiovascular Space
Lauren D. Breite, Mackenzie Steck, Brandon Tate Cutshall, Samarth P. Shah, Brandon E. Cave
Current Problems in Cardiology.2021; 46(3): 100736. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Safety and Benefits of Noninsulin Antihyperglycemic Drugs for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Part 2
Srikanth Yandrapalli, Aaqib Malik, Adam Horblitt, Gayatri Pemmasani, Wilbert S. Aronow, William H. Frishman
Cardiology in Review.2020; 28(5): 219. CrossRef - Effects of antidiabetic drugs on left ventricular function/dysfunction: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Da-Peng Zhang, Li Xu, Le-Feng Wang, Hong-Jiang Wang, Feng Jiang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor compared with sulfonylurea in combination with metformin: cardiovascular and renal outcomes in a propensity-matched cohort study
Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Juneyoung Lee, Jae Hyun Bae, Jee Hyun An, Hee Young Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Cardiovascular Risks of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors: Analyses of Real-world Data in Korea
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Bongseong Kim, Hae Sol Shin, Jinhee Lee, Hansol Choi, Hyeon Chang Kim, Dae Jung Kim
Korean Circulation Journal.2018; 48(5): 395. CrossRef - Worsening Heart Failure During the Use of DPP-4 Inhibitors
Milton Packer
JACC: Heart Failure.2018; 6(6): 445. CrossRef - Resistance exercise improves cardiac function and mitochondrial efficiency in diabetic rat hearts
Tae Hee Ko, Jubert C. Marquez, Hyoung Kyu Kim, Seung Hun Jeong, SungRyul Lee, Jae Boum Youm, In Sung Song, Dae Yun Seo, Hye Jin Kim, Du Nam Won, Kyoung Im Cho, Mun Gi Choi, Byoung Doo Rhee, Kyung Soo Ko, Nari Kim, Jong Chul Won, Jin Han
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology.2018; 470(2): 263. CrossRef - Do DPP-4 Inhibitors Cause Heart Failure Events by Promoting Adrenergically Mediated Cardiotoxicity?
Milton Packer
Circulation Research.2018; 122(7): 928. CrossRef - Comparative safety for cardiovascular outcomes of DPP-4 inhibitors versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes
Hyouk-Jun Chin, Jin Hyun Nam, Eui-Kyung Lee, Ju-Young Shin
Medicine.2017; 96(25): e7213. CrossRef - Effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor in insulin-resistant rats with myocardial infarction
Nattayaporn Apaijai, Tharnwimol Inthachai, Suree Lekawanvijit, Siriporn C Chattipakorn, Nipon Chattipakorn
Journal of Endocrinology.2016; 229(3): 245. CrossRef - The current role of thiazolidinediones in diabetes management
Christos V. Rizos, Anastazia Kei, Moses S. Elisaf
Archives of Toxicology.2016; 90(8): 1861. CrossRef - Alternative Interventions to Prevent Oxidative Damage following Ischemia/Reperfusion
Simón Quetzalcoatl Rodríguez-Lara, Ernesto German Cardona-Muñoz, Ernesto Javier Ramírez-Lizardo, Sylvia Elena Totsuka-Sutto, Araceli Castillo-Romero, Teresa Arcelia García-Cobián, Leonel García-Benavides
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Lessons learned from cardiovascular outcome clinical trials with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors
Teresa Vanessa Fiorentino, Giorgio Sesti
Endocrine.2016; 53(2): 373. CrossRef - Letter: Increased Risk of Hospitalization for Heart Failure with Newly Prescribed Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Pioglitazone Using the Korean Health Insurance Claims Database (Diabetes Metab J2015;39:247-52)
Dae Ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(4): 348. CrossRef - Response: Increased Risk of Hospitalization for Heart Failure with Newly Prescribed Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Pioglitazone Using the Korean Health Insurance Claims Database (Diabetes Metab J2015;39:247-52)
Sunghwan Suh, Gi Hyeon Seo, Chang Hee Jung, Mee-Kyoung Kim, Sang-Man Jin, You-Cheol Hwang, Byung-Wan Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(4): 350. CrossRef - Cardiovascular, renal and gastrointestinal effects of incretin-based therapies: an acute and 12-week randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, mechanistic intervention trial in type 2 diabetes
Mark M Smits, Lennart Tonneijck, Marcel H A Muskiet, Trynke Hoekstra, Mark H H Kramer, Indra C Pieters, Djuna L Cahen, Michaela Diamant, Daniël H van Raalte
BMJ Open.2015; 5(11): e009579. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Alarms: Is Heart Failure Caused by a Class Effect?
Yong-ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(3): 204. CrossRef
- Cardioprotective effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors versus sulfonylureas in addition to metformin: A nationwide cohort study of patients with type 2 diabetes

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





